Understanding The Classification Of Antidepressants: A Deep Dive
When life feels like it’s pulling you under, antidepressants can be a lifeline. These medications are designed to help balance the chemicals in your brain, giving you a fighting chance against depression and anxiety. But not all antidepressants are created equal. The classification of antidepressants is a crucial aspect to understand if you're considering this treatment route. Let's break it down, shall we?
Imagine walking into a pharmacy and being bombarded with options. Which one is right for you? That's where understanding the classification of antidepressants comes into play. It’s not just about picking a pill; it’s about finding the one that works best for your unique brain chemistry. And trust me, that’s no small feat.
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s get one thing straight: antidepressants are not a one-size-fits-all solution. They come in different shapes, sizes, and chemical compositions. Knowing the classification of antidepressants will help you and your doctor make an informed decision about your treatment plan. So, buckle up because we’re about to embark on a journey through the world of mental health medication.
Read also:Masiela Lusha Nudes The Truth Behind The Controversy And What You Need To Know
What Are Antidepressants and Why Do We Need Them?
Antidepressants are medications that help treat depression, anxiety disorders, and sometimes even chronic pain. They work by altering the levels of certain chemicals in your brain, like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. These chemicals play a big role in regulating your mood, so when they’re out of whack, it can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and even physical symptoms.
Now, you might be wondering, why do we need so many different types of antidepressants? Well, here's the thing: everyone’s brain is different. What works for one person might not work for another. That’s why scientists have developed various classifications of antidepressants, each targeting different neurotransmitters and pathways in the brain.
Think of it like this: your brain is like a city, and neurotransmitters are the traffic lights. If the traffic lights aren’t working properly, the city becomes chaotic. Antidepressants are like the traffic cops, helping to restore order and keep things running smoothly. But just like there are different types of traffic cops, there are different types of antidepressants.
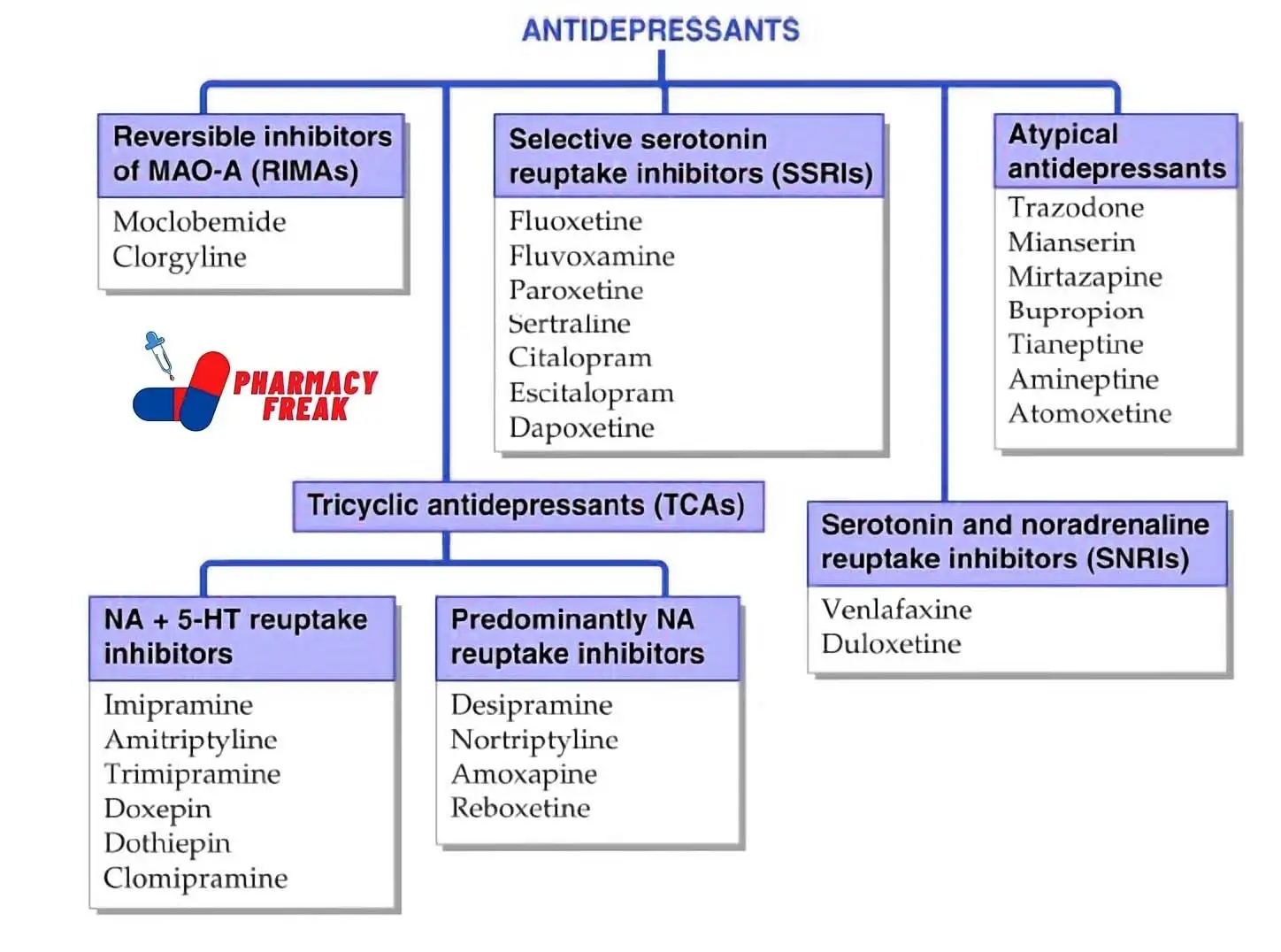
The Classification of Antidepressants: Breaking It Down
Let’s get into the meat of the matter. Antidepressants are generally classified into several categories, each with its own unique mechanism of action. Here’s a quick rundown:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are probably the most well-known class of antidepressants. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in your brain. Serotonin is often referred to as the “happy chemical” because it contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness. Some common SSRIs include:
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Citalopram (Celexa)
SSRIs are usually the first line of treatment for depression because they tend to have fewer side effects compared to other classes of antidepressants.
Read also:Notti Osama Video Death The Untold Story Behind The Controversy
Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are similar to SSRIs, but they also increase the levels of norepinephrine in addition to serotonin. Norepinephrine is another neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood regulation. Some popular SNRIs include:
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Venlafaxine (Effexor)
SNRIs are often used when SSRIs aren’t effective or when someone is experiencing chronic pain alongside depression.
Other Classes of Antidepressants
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
TCAs are one of the oldest classes of antidepressants. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. However, they tend to have more side effects than newer classes like SSRIs and SNRIs. Some examples of TCAs include:
- Amitriptyline
- Imipramine
TCAs are usually reserved for cases where other treatments haven’t worked.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
MAOIs are another older class of antidepressants. They work by inhibiting an enzyme called monoamine oxidase, which breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Some common MAOIs include:
- Phenelzine (Nardil)
- Tranylcypromine (Parnate)
MAOIs can be effective, but they require dietary restrictions because they can interact with certain foods and medications.
Atypical Antidepressants
Atypical antidepressants don’t fit neatly into any of the other categories. They work in various ways to affect neurotransmitter levels in the brain. Some examples include:
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin)
- Mirtazapine (Remeron)
These medications are often used when other treatments haven’t been successful or when someone has specific symptoms that other antidepressants don’t address.
How Are Antidepressants Classified?
The classification of antidepressants is based on how they affect the brain’s neurotransmitter systems. Each class targets different neurotransmitters and pathways, which is why they’re used for different types of mental health conditions. For example, SSRIs are great for treating depression and anxiety, while TCAs might be better for treating chronic pain alongside depression.
It’s important to note that not all antidepressants are suitable for everyone. What works for one person might not work for another, which is why it’s crucial to work closely with your doctor to find the right medication for you.
Side Effects and Considerations
Like any medication, antidepressants come with potential side effects. The type and severity of side effects can vary depending on the class of antidepressant. Some common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Weight gain
- Sexual dysfunction
It’s important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks when deciding whether to start an antidepressant. Your doctor can help you understand what to expect and how to manage any side effects that arise.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Antidepressant
Choosing the right antidepressant involves considering several factors, including:
- Your specific symptoms
- Your medical history
- Potential interactions with other medications
- Side effect profile
- Cost and availability
Your doctor will take all of these factors into account when recommending a treatment plan. It’s a collaborative process, and your input is valuable in making the final decision.
How Long Does It Take for Antidepressants to Work?
One of the most common questions people have about antidepressants is how long it takes for them to start working. The answer isn’t straightforward because it can vary depending on the individual and the specific medication. Generally, most people start to notice improvements in their symptoms within 2-4 weeks of starting an antidepressant.
It’s important to be patient and give the medication time to work. If you don’t see any improvement after a few weeks, talk to your doctor. They might adjust your dosage or switch you to a different medication.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Antidepressant for You
Understanding the classification of antidepressants is key to finding the right treatment for your mental health needs. From SSRIs to MAOIs, each class of antidepressant has its own unique benefits and potential side effects. By working closely with your doctor, you can find the medication that works best for you.
Remember, taking antidepressants is not a sign of weakness. It’s a proactive step toward improving your mental health and quality of life. If you’re considering this treatment option, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance.
And hey, if you found this article helpful, why not share it with someone else who might benefit from it? Knowledge is power, and the more we talk about mental health, the better off we’ll all be.
Table of Contents
- What Are Antidepressants and Why Do We Need Them?
- The Classification of Antidepressants: Breaking It Down
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Other Classes of Antidepressants
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Atypical Antidepressants
- How Are Antidepressants Classified?
- Side Effects and Considerations
- Factors to Consider When Choosing an Antidepressant
- How Long Does It Take for Antidepressants to Work?
- Conclusion: Finding the Right Antidepressant for You